Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body can not regulate blood sugar levels. It can lead to a range of complications, including cardiovascular disease and nerve damage.
There are two Types of Diabetes as Follows.
Type 1 Diabetes
- Cause: Autoimmune reaction — the body attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Detection: Usually starts in childhood or adolescence (but can develop in adults too).
- Insulin Production: Little to none. The body can't produce insulin.
- Treatment: Requires daily insulin injections or use of an insulin pump.
- Risk Factors: Genetic predisposition; not related to lifestyle.
- Prevention: Not preventable.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Cause: Insulin resistance — the body doesn't use insulin properly; often combined with gradual insulin production decrease.
- Detection: Typically in adults over 40, but increasingly common in younger people due to lifestyle.
- Insulin Production: Yes, but it's not used effectively.
- Treatment: Often managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
- Risk Factors: Overweight, inactivity, poor diet, family history.
- Prevention: Often preventable or delayable with healthy habits.
Monitoring Blood Sugar & A1C
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Fingerstick Test (Glucometer):
- Prick your finger using a lancet.
- Use a test strip in a blood glucose meter.
- Get an immediate reading.
Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM):
A sensor is placed under your skin.
It measures glucose continuously, sending data to a device or phone.
When to Check:
Before meals.
1-2 hours after eating.
Before bed.
When feeling symptoms (e.g. shaky, sweaty, dizzy).
More frequently if insulin-dependent.
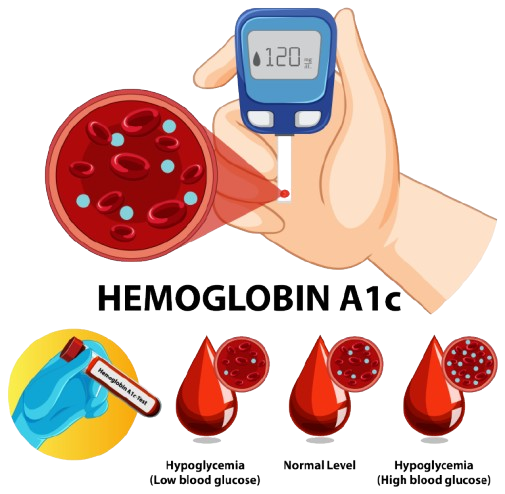
A1C Test (Hemoglobin A1C)
This reflects your average blood sugar level over the past 2–3 months.
How it’s Done:
Requires a blood draw (fingerstick or lab).
Typically done every 3 months (or every 6 months if stable).
Target A1C (for most people with diabetes):
Below 7% (talk to your doctor—individual goals vary).
Tips for Better Monitoring:
Keep a log (or use an app) to track levels, meals, exercise, and medication.
Calibrate your CGM if needed.
Review your data regularly with your healthcare provider.
Watch for patterns, not just individual numbers.
Lifestyle & Dietary Precautions
Lifestyle
Exercise:
Aim for 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week (walking, biking, swimming).
Add strength training 2–3 times a week.
Movement helps lower blood sugar and boost insulin sensitivity.
Sleep:
Get 7–9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
Poor sleep = higher insulin resistance.
Stress Management:
Try meditation, deep breathing, journaling, or light stretching.
Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels.
Avoid Smoking & Limit Alcohol:
Smoking increases risk of complications.
Drink in moderation (if allowed by your care team).
Dietary
Eating Habits:
High-fibre carbs: whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, tofu, fish, eggs.
Healthy fats: avocado, nuts, olive oil.
Low-glycemic index foods: berries, sweet potatoes, lentils.
Bad Habits:
Sugary drinks (soda, juice, sweet tea).
Processed/refined carbs (white bread, pastries).
Trans fats (some fried/packaged foods).
Excess salt and saturated fats.
Smart Habits:
Eat regular meals/snacks to avoid spikes and crashes.
Portion control: Use a plate method (½ veggies, ¼ protein, ¼ carbs).
Stay hydrated with water.

